HIV/AIDS Pandemic
About two-thirds (67%) of all people with HIV worldwide are in Sub-Saharan Africa. In 2021:
- About 38.4 million people were living with HIV
- 670,000 adults and children were newly infected
- 280,000 people died from the disease
Worldwide in 2021:
- 650,000 people died of AIDS
- About 1.5 million people were newly infected
In 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 39 million people were living with HIV worldwide.
History of PEPFAR
On May 27, 2003, the United States Leadership Against Global HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Act of 2003 was signed into law (PDF - 214 KB). This created the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the largest health program worldwide for a single disease. The plan emphasizes a “whole government” response to provide the most effective interventions. Many federal agencies are involved in PEPFAR’s implementation, including:
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)
- U.S. Department of State U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
- U.S. Department of Defense
- Peace Corps
- Angola
- Asia Regional (Burma, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Laos, Nepal, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Tajikistan, Thailand)
- Botswana
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Western Hemisphere Region (Barbados, Brazil, El Salvador, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Jamaica, Nicaragua, Panama, Trinidad & Tobago, Suriname)
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Eswatini
- Ethiopia
- Haiti
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Tanzania
- Uganda
- Ukraine
- Vietnam
- West Africa Region (Burkina Faso, Ghana, Liberia, Mali, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Togo)
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
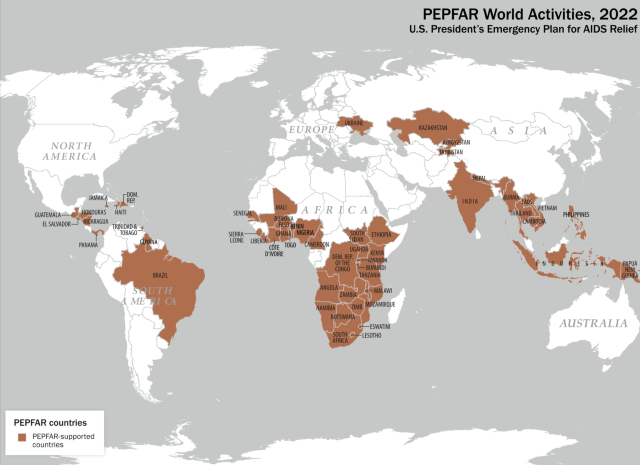
PEPFAR's first focus was on emergency response. PEPFAR gave $15 billion over a five-year period to 15 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean to:
- Provide treatment to 2 million HIV-infected people
- Prevent 7 million new HIV infections
- Care for 10 million people infected and affected by HIV/AIDS, including:
- More than 4 million orphans and vulnerable children
- Treatment to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission for nearly 16 million pregnancies
PEPFAR was reauthorized in 2008, with up to $48 billion over five years to combat global HIV/AIDS, TB, and malaria. This second phase of PEPFAR focused on sustainability through local partnerships with goals to:
- Provide treatment for at least 3 million people
- Prevent 12 million new infections
- Care for 12 million people, including 5 million orphans and vulnerable children
U.S. government teams in 22 countries developed and signed Partnership Frameworks with host country governments. The Frameworks cemented mutual accountability and collaboration for priority HIV/AIDS activities. These agreements marked a hallmark event between 2009 and 2012.This launched a new era of health systems strengthening activities with partner governments. To increase the impact of PEPFAR's investments, there was a focus on:
- Scaling up access to antiretroviral therapy (ART)
- Preventing mother-to-child transmission
- Voluntary medical male circumcision
In 2013, PEPFAR entered its third phase, ‘Controlling the Epidemic,’ with a mandate to reach UNAIDS’ ambitious 90-90-90 goal: 90% of people with HIV diagnosed, 90% of them on ART, and 90% of them virally suppressed by 2020.
This approach was driven by data to strategically target geographic areas and populations for maximum impact. The President’s FY 2016 budget request for PEPFAR was $6.5 billion with bilateral support provided to 41 countries and regional programs in Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Europe, the Americas, and the Caribbean.
PEPFAR 3.0
- Impact: efficient and effective control of the HIV epidemic
- Efficiency: increased transparency, oversight, and accountability across PEPFAR
- Sustainability: sustainable governance, increased country funding and local partner implementation
- Partnership: renewed national and global commitments to an AIDS-free generation
- Human Rights: promotion and protection of human rights for all, including LGBT people and other vulnerable populations